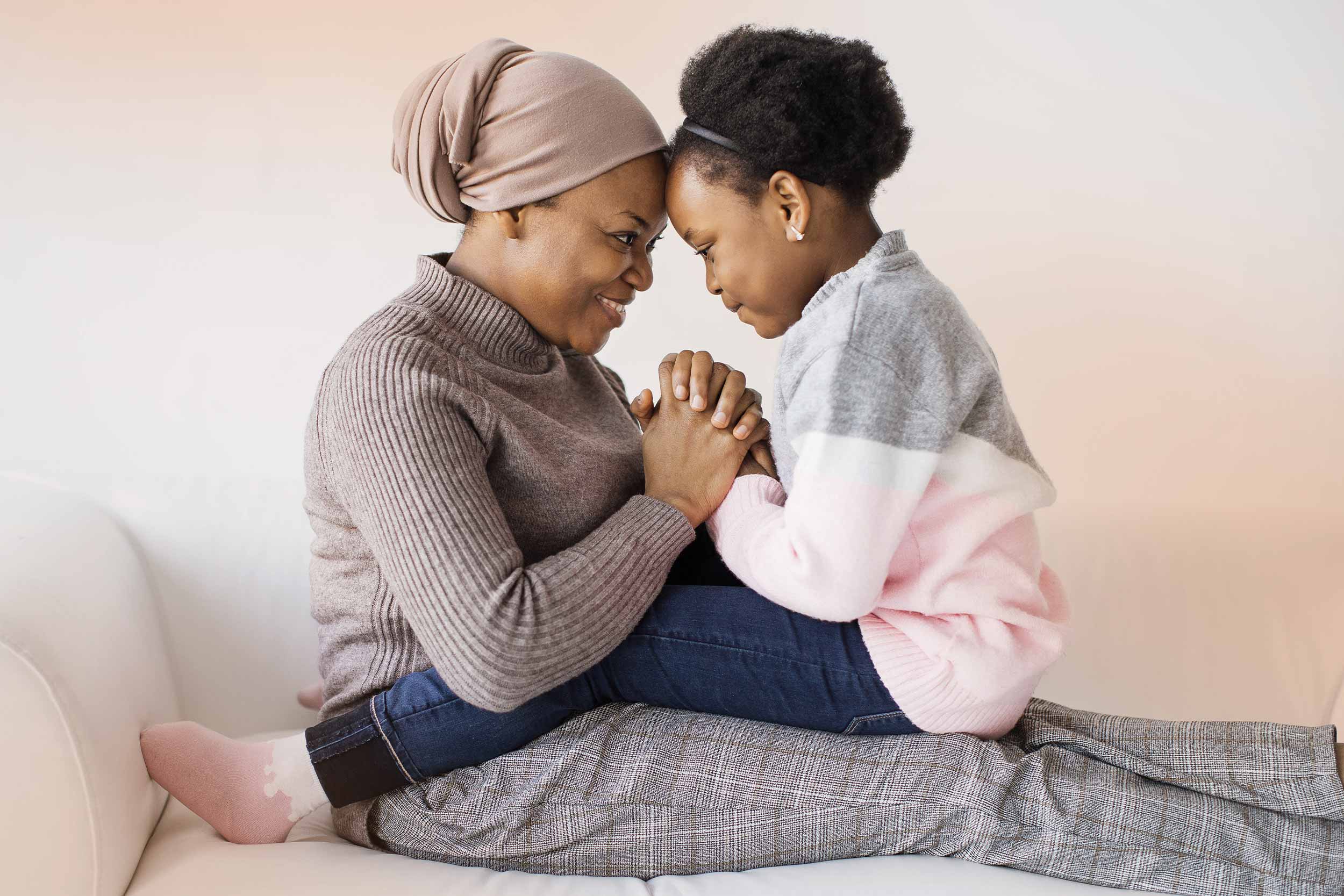
It’s the latest conclusion from a multi-year longitudinal psychology study that has followed the development of a large group of people from childhood to adulthood.
Stern said she and her colleagues followed 184 diverse teens from age 13 into their mid-30s. They filmed each teen and their mother discussing a problem the teen needed help with. The researchers noted how much empathy the mothers exhibited to their children.
“Then every year from age 13 to 19, the teens did that same type of discussion task with their closest friend and we could observe how much teens were showing empathy when their best friend was having a problem,” Stern explained.
Years later, the teens who went on to have children of their own, relayed their parenting behavior to the researchers as well as their own children’s empathy when those children were between 3 and 8 years old.
“The things we are looking for regarding empathy – and this is both in moms and then in their teens when they’re talking to their friends – were things like emotional engagement – so leaning forward in the conversation, nodding, showing interest in what the person is saying,” Stern said. They also noted demonstrations of emotional support like validating a person’s feelings.
“I think probably the most novel piece of this study, is linking anything having to do with friendships from adolescence to later parenting behavior,” Stern said. “That hasn’t been done before.”
What if a parent is not seeing empathy in their teen? “I really believe that empathy is a teachable skill,” Stern said. “One of the components of that is trying to help teens reflect on their own emotions and other people's emotions.”
If, for example, a parent sees their teen is indifferent to a friend who’s struggling, they can ask how the friend is doing and offer prompts like, “I would be really sad if I were struggling. I wonder if they need some help.”
“And then help the teen brainstorm what might be most helpful,” Stern offered. “It could be that they don’t really know how to provide support in that particular instance and they just need a little bit of guidance.
“A parent can say ‘Hey, it would be really nice if you checked in on Anthony, gave him a call or text to see how he’s doing. I’m sure he’d appreciate that.’”
The new study, titled “Empathy Across Three Generations: From Maternal and Peer Support in Adolescence to Adult Parenting and Child Outcomes,” will be published in the journal Child Development.