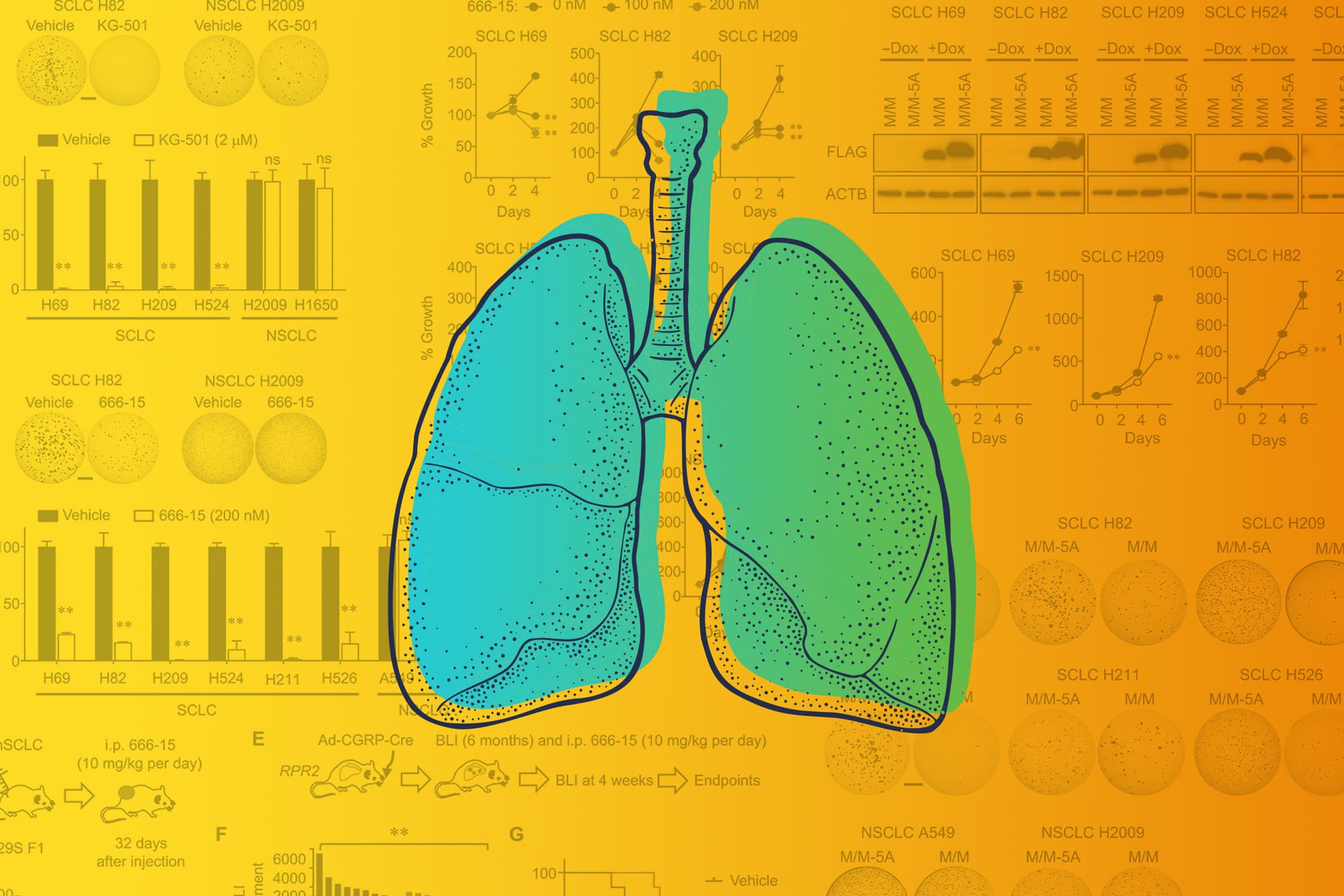
An unexpected discovery at University of Virginia Cancer Center has allowed scientists to halt the development of small-cell lung cancer in lab mice, and the surprise finding could open the door to a new treatment approach in people.
The researchers, led by UVA’s Kwon-Sik Park and John H. Bushweller, were seeking to understand the role of a mutation in the EP300 gene in the formation of small-cell lung cancer tumors. Their experiments revealed that the gene makes a protein with surprising properties that can both foster or prevent the development of small-cell lung cancer. By preventing the gene from acting as a tumor-promoter, the researchers were able to stop the cancer from forming and spreading. This held true in both cell samples and lab mice.

Kwon-Sik Park is a researcher in the UVA School of Medicine’s Department of Microbiology, Immunology and Cancer Biology. (UVA School of Medicine photo)
The protein’s essential role in tumor formation makes it an enticing target for researchers seeking to development new treatments for small-cell lung cancer, an exceptionally dangerous form of cancer. Overall five-year survival for patients diagnosed with the disease is only about 7%.
“The most remarkable aspect of our findings is that we explained the unique vulnerability of EP300 at the molecular level, down to a single amino acid,” said Park, of the School of Medicine’s Department of Microbiology, Immunology and Cancer Biology. “Given the frequent EP300 mutations found in a wide range of cancer types, I hope that the concept of targeting the EP300 KIX domain will have a more general applicability for cancer therapy.”
About Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Small-cell lung cancer is responsible for approximately 13% of lung cancer diagnoses. Patients typically have better outcomes when it is caught early, before it has spread outside the lung, but it is a fast-growing cancer and is often discovered after it has already spread. Smoking is a major risk factor. Current treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation and immunotherapy, but, for most patients, treatments do not cure the cancer. That means better options are urgently needed.

John H. Bushweller is a researcher in UVA’s Department of Molecular Physiology and Biological Physics. (UVA Health photo)
UVA’s new findings point to a potential new approach. Park and his team made their surprise discovery while investigating the role of the EP300 gene in the development of small-cell lung cancer using genetically engineered mouse models. Remarkably, they found the protein the gene makes could both promote and suppress tumor formation. One component, or “domain,” of the protein appeared to foster cancer development, while another appeared to impede it.
The scientists further investigated the tumor-promoting domain, called KIX, and found it was essential for small-cell lung cancer development. The cancer couldn’t exist without it. The cancer, it turned out, had to get its KIX.
That suggests that targeting KIX could offer a way to treat small-cell lung cancer in patients, the scientists say. In a new scientific paper outlining their findings, they call KIX a “unique vulnerability” in small-cell lung cancer.
To explore this newfound vulnerability, Park immediately turned to UVA’s Bushweller and Tim Bender, who previously had considered targeting the KIX domain. A fruitful collaboration instantly ensued.
“Based on this data, we are quite excited to pursue the development of a drug targeting the KIX domain, as this will likely have multiple applications for cancer treatment, particularly for small-cell lung cancer and leukemia,” Bushweller, of UVA’s Department of Molecular Physiology and Biological Physics, said.
The researchers were pleased that their collaboration has produced such a promising lead in the effort to develop better therapies for small-cell lung cancer.
“This study was one of the best examples for the interdisciplinary collaborations happening at UVA, spearheaded by talented and hardworking postdocs Kee-Beom Kim and Asish Kabra,” Park noted.
Shedding light on the causes of cancer and pioneering better ways to treat it are urgent missions of the UVA Cancer Center, which on Feb. 1 became one of only 52 cancer centers in the country to be designated as a Comprehensive Cancer Center by the National Cancer Institute. The designation recognizes elite cancer centers with the most outstanding cancer programs in the nation. Comprehensive Cancer Centers must meet rigorous standards for innovative research and leading-edge clinical trials.
UVA Cancer Center is the only Comprehensive Cancer Center in Virginia.
Findings Published
The researchers have published their findings in the scientific journal Science Advances. The research team consisted of Kim, Kabra, Dong-Wook Kim, Yongming Xue, Yuanjian Huang, Pei-Chi Hou, Yunpeng Zhou, Leilani Miranda, Jae-Il Park, Xiaobing Shi, Timothy P. Bender, Bushweller and Park.
The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health, grants R01CA194461, U01CA224293, R01GM100776, R56AI108767, R01CA204020, P30CA044579 and P30CA008748; a UVA “Three Cavaliers” grant; and an Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma Research Foundation grant.
To keep up with the latest medical research news from UVA, subscribe to the Making of Medicine blog.
Media Contact
Article Information
February 24, 2022
/content/some-good-news-surprise-discovery-suggests-new-treatment-deadly-lung-cancer